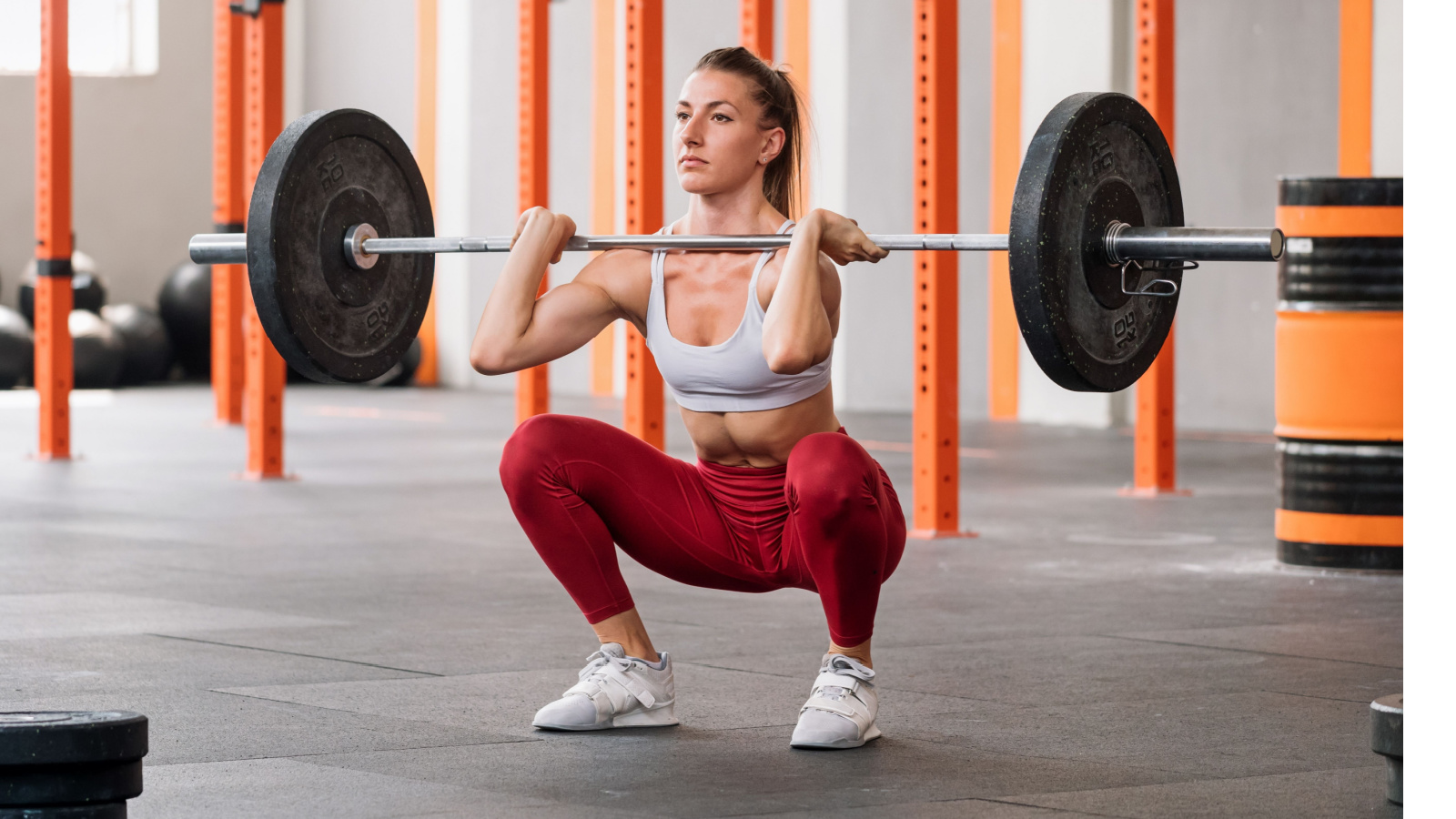
While squats are the king choice for leg day, they’re also the bane of many lifters’ existence. Some people simply don’t squat due to negligent programming while they bias toward relatively easier upper body training. Others might not squat because they’ve never learned proper technique and they can’t get comfortable with the movement.

If you’re in either of these categories, you’re in luck. Sometimes it helps to consider similar alternatives to the basic squat, so you can get all the benefits of the exercise using a variation that better suits your individual needs.
Plus, it can break up the monotony of a potentially stale workout program if you’ve hit a plateau. Changing things up to find what works for you is half the battle for long-term results and one or more of these may be the game changer you need.
Best Squat Variations
Front Squat
The front squat is a classic alternative to the more common and ubiquitous back squat. As a whole, the front squat can allow similar loading, as long as your mobility is on point. It can also promote a longer range of motion with less potential for lumbar spine injury.
Because the front squat is a more “athletic” variation compared to many other squats, it relies on coordinating strength from both your upper and lower body. In certain fitness worlds, like Olympic lifting or CrossFit, it’s considered the go-to squat variation.
When to Do it
If you’re looking to hit the quads a bit harder or achieve a deeper squat with a long range of motion (either by choice or due to immobility in your back squat), the front squat is for you. Many lifters’ anthropometry and leverages don’t suit the back squat, but are better suited to the front squat due to its counterbalancing attributes. If you’ve got very long femurs or long legs overall, you owe it to your lower body development to give these a shot.
How to Do it
There are two classic grips to hold the barbell on the front of the body while squatting. The relatively easier way is to use a cross-armed grip, also known also as the “California” style. Set a barbell in a squat rack and step up with your throat close to the bar. Cross your arms over one another — place the fingers of each hand on top of the bar near the opposite shoulder.
Keep your elbows high and hold the bar place with the thumb and first finger of each hand. This will also help to block the bar from rolling forward down the shoulders. Step out of the rack with your upper body in a strong position, set a comfortable-width stance, and proceed to squat.
The second option is using a clean-grip rack position — holding the barbell across the fronts of your shoulders with a fully closed grip. This is a more stable and relatively safer variation but requires a lot more mobility and flexibility, especially in your thoracic region (upper back), wrists, and shoulders.
To determine if you can comfortably use the clean-grip, try to touch each shoulder with the same-side hand while standing. If you can, you likely have the mobility to do these, maybe with some practice mixed in. When using a clean-grip, aim to keep your elbows high at all times, especially during the lowering phase.
Zercher Squat
The Zercher squat moves the barbell from being supported via an axial load (on your spine) and places the onus on your arms instead. That means huge accountability for your core — both from the front (your abs) and the back (particularly your lower back) — to brace and stabilize your spine as the movement progresses.
The Zercher squat isn’t for the faint of heart. It’s a challenging squat movement that can even be simply uncomfortable to perform. It’s best done early in the workout when you’re fresh, compared to later on when your shoulders, arms, and core are fatigued.
When to Do it
Because the Zercher squat uses an appendicular load (supporting the weight with your arms), the movement is a great way to begin a core-focused workout. Moreover, lifters who have issues getting their arms and shoulders into position for standard barbell squats — think about how some shoulder injuries can prevent holding the bar during a back squat — the Zercher squat can be a suitable alternative. Aside from these stipulations, these can be added to any training session as a worthy challenge for any lifter up for the task.
How to Do it
Performing Zercher squats requires placing the barbell in the crook of your arms, so it’s being carried and supported by your elbows. Set up a barbell at waist-level. When placing your elbows under the bar to unrack it, avoid an arm width that’s too narrow. That will lead to limited stability, likely causing the bar to tip one way or the other. Aim to keep your knuckles facing the ceiling at all times. This way, the bar will be positioned squarely between your upper and lower arm, rather than falling toward your forearms.
Holding your hands together while performing the movement may be helpful to fulfill the above cues. As you squat, keep the weight relatively close to your body. In the bottom position, let your elbows rest between your thighs and maintain as vertical a torso as possible. Drive up to the top, and repeat.
For added comfort, try using “fat grips” or thick padding on the bar where your forearms will go. The added surface area will disperse some of the loading, which should take some pressure off your elbow joint.
Overhead Squat
Of all the squat variations of this list, the overhead squat requires the most prerequisite mobility and stability. The movement simply cannot be done without proper joint integrity at your shoulders, hips, knees, and ankles. You also need good extension through your thoracic and lumbar spine.
Doing this exercise forces a lifter to be highly accountable to factors like tempo and technique, while respecting physics, the weight lifted, and the multitude of muscles involved. There’s no arguing with the laws of the universe. Anything out of sorts will cause the barbell to come down. With all of this said, this movement should be reserved for those who have uninhibited ranges of motion in their load bearing joints.
When to Do it
Especially if you’re an Olympic weightlifter performing the snatch or the clean & jerk, the overhead squat can improve strength in the catch or push jerk phases of those lifts. The overhead squat should be done without the presence of any muscular fatigue, so programming it first in the daily order of exercises is a wise choice.
How to Do it
An overhead squat requires a snatch-grip to secure the bar. To find your snatch grip, stand tall while holding the barbell with a palms-down grip. Gradually adjust your grip wider and wider until the bar naturally sits in your hip fold. Next, raise the bar overhead to full extension, maintaining that hand width.
Get into your ideal squat stance and squeeze “outward” on the bar with both hands to create tension through your entire back. As you descend into a squat, aim to never let the bar fall outside of your footprint — either forward or backward. The bar should descend and ascend in a generally straight line. Move slowly and keep reps on the lower end.
Kang Squat
The Kang squat can be used as its own exercise or as a premier mobilization drill, warm-up, and pattern developer. Its biggest benefit is that it uniquely segments the squat into a more posterior chain-biased movement pattern. This emphasizes a good range of motion and bottom-end stability.
Another great thing about the Kang squat is the fact that it places the hamstrings in a loaded stretch, which can allow them to release tension in the pelvis due to eccentric lengthening. That can mean a deeper and more comfortable squat that also helps cranky knees, due to improved activation of the hamstrings.
When to Do it
Use the Kang squat in the first half of a squat-focused workout. This approach will torch your posterior chain (hamstrings and glutes) and make those muscles more available for activation during squats later in the session. Starting your leg workout with Kang squats can also act as a good CNS primer for any larger compound (multi-joint) movement.
How to Do it
The Kang squat begins similar to a good morning — performing a deep hip hinge with slightly bent legs, holding the bar on your upper traps. It’s essential to place tension across the bar by “pulling it apart” to keep the barbell in place.
After your hinge reaches its limit, it’s time for the knees to enter the picture by allowing a full knee bend, enabling your glutes to descend into a deep squat. Next, come out of the hole by raising your hips back into the good morning position. Your glutes and lower back extend your body back to its upright starting point. Try to pause in each phase to make the movement concise and segmented. Focus on sets of four to six reps.
Heels-Elevated Dumbbell Squat
Whenever mobility is lacking, or if your goal is to really hammer your quads, it may not be in the cards to simply rely on dorsiflexion (ankle mobility) or a front-positioned load to get the job done.
If you’re a lifter with stiff ankles, or if you have great mobility but want to really make your knees and quads bionically super-strong, elevating your heels and holding dumbbells at your sides is the squat variation for you.
When to Do it
This movement is less of a “big lift” compared to other large movements like barbell-loaded exercises, leg presses, or deadlifts, so it can actually happen second or later in your workout. Doing so will also make your quadriceps more targeted, especially if other leg muscles are fatigued. Using dumbbells rather than a barbell also keeps the movement more focused on your lower body with relatively less involvement from your upper body.
How to Do it
If possible, use a dedicated slant board rather than simply elevating your heels on the edges of weight plates. Having your entire foot on a slope makes a major difference due to the angle of your metatarsals, which affect your arches and weight distribution.
This movement will definitely promote a rock-bottom range of motion, which means maximal knee flexion for a massive hit to your quads. The quads generally respond well to high reps, so that should be the aim for this movement. Pump out sets of 10-15 reps and try to enjoy the burn. Make sure not to rush the tempo — more time under tension can mean more muscle growth. (1)
Goblet Squat
Goblet squats are a go-to movement for anyone, especially beginners, looking to improve their squatting technique. Not only is the exercise accessible for every lifter, but it’s front loaded, making counterbalancing and stability easier. Since your elbows are positioned downward and the weight’s position near your torso is slightly adjustable, it usually promotes a great depth with minimal modifications necessary.
In general, lifters should aim to become competent enough to perform relatively heavy goblet squats to start out and build a foundation, and then transition to a barbell back squat.
When to Do it
Novice lifters can use this as their bread and butter squat to really nail down the patterning and get a great lower body hit. Using this exercise on its own, or as part of a superset with another leg exercise, is effective.
It’s unlikely you’ll be able to use maximum weights, as most gyms don’t have extremely heavy dumbbells (and your strength will eventually exceed the limit). For that reason, using the goblet squat as a muscle-building tool for moderate to higher repetitions is the right call.
How to Do it
Hold a kettlebell or dumbbell in front of you at shoulder-height using both hands. Keep the weight in this position, set your feet for your ideal squat stance, and sit down.
To get deep and feel comfortable, you may feel better pushing the weight a couple of inches away from your torso as you descend. This is especially useful if you’re lacking mobility at the ankle or hip joints. Focus on using a slower speed on the way down and a stronger, powerful speed coming up. Focus on sets of eight to 10 reps.
Box Squat
Squatting to a box does a few unique things. First, it keeps you accountable to a consistent target so there’s no margin for error or questionable depth. Secondly, it encourages a dead stop for no transfer of energy or use of the stretch reflex to “sling” your way out of the bottom position using momentum or elastic forces rather than muscular control.
Lastly, the box squat can hit your posterior chain a bit harder and salvage your knees from unwanted joint pain. Using the box helps to eliminate forward migration of the shin and prevents you from reaching too deep a position which could require more knee extension.
When to Do it
The box squat is typically treated as strength-focused movement. Perform them heavy, with standard principles of progressive overload applying — adding repetitions or increasing the weight each workout. Box squats can also occupy a high-volume role in your workout, using relatively low rep ranges, plenty of sets, and focusing on hip drive and overall technique. In either case, perform the box squat as the first movement of the workout.
How to Do it
When box squatting, it’s typical to use a sturdy box that puts your upper thigh parallel to the ground, not lower, when you’re in the bottom of the squat. This becomes even more important since your body’s geometry needs to slightly change from that of a typical back squat.
Use a low-bar squat position, to accommodate for keeping your shins much more vertical, which will force your torso to lean forward more than usual. Your foot width will be a bit wider — at least one extra step to the side — to allow for the low-bar position and to suit the box width.
Focus on remaining tight while gently, but fully, sitting down on the box. After sitting down, drive hard with your hips — upward and then forward— to create the posterior chain tension necessary to get out of the hole. Sets of three to five reps is ideal for this exercise.
Hatfield Squat
The Hatfield squat makes use of a safety bar and the squat cage in a unique way. The squat is actually performed “hands free” while using the rack itself as a guide to encourage more repetitions with heavier weights.
The support of the rack will also take some of the focus away from your upper body to shift attention to your lower body. The results is better technique, a stronger pump, and deep range of motion. Note: You cannot perform this exercise with a standard barbell.
When to Do it
This is more of a hypertrophy training tool and they can be added to a lower body workout geared toward building muscle. This movement is most conducive to higher reps, while giving your muscles a chance to push themselves a bit further than normal with heavier weight.
How to Do it
The one non-negotiable piece of equipment needed for a Hatfield squat is a safety bar. Place the loaded bar on the rack, get into the pads, and carefully step out from the rack. Place both hands on either support beam around waist height. The safety bar will be balancing on your upper back, but it should be secure due to its handles and offset center of gravity.
Squat down using the support beams for assistance. Keep your torso upright, but really use your hands to guide your way up and down. It’s okay if you don’t come to an absolute full extension — the name of the game is getting a few more reps in. You can use a slightly faster pace as long as you remain in control of the weight. Focus on sets of 10-15 reps, and don’t shy away from heavier than normal weight for said rep range. You should be able to do it with the hand-supported assistance.
Skater Squat
A list of squat variations wouldn’t be complete without highlighting a unilateral exercise, and one of the most important ones that doesn’t lend itself to cheating is the skater squat. This enforces stability through your hip and knee joint and makes your glutes, quads, and ankles work overtime to stabilize the leg, making this exercise possible.
Especially if you’re suffering from bilateral imbalances or joint issues in your hips, knees, or ankles, this variation belongs in your program. It likely won’t take much more than bodyweight to get a major training effect from them, so they can be performed nearly anywhere or anytime.
When to Do it
Positioning this exercise as an accessory movement in a squat workout, as a primer and warm-up before a lower body workout, or as its own prioritized exercise on a “weak link” training day is all fair game. What matters the most is that it gets done. A good skater squat is an indicator of lower body health and strength.
How to Do it
Stand with on one foot planted on the ground and the opposite leg bent roughly 90-degrees with the foot in the air. Lean forward slightly and extend your arms in front of you as a natural counterbalance. Making fists can also help with stability. Descend slowly, aiming to gently touch the back knee to the ground. On contact, drive with your front leg — don’t push off with the knee, shin, or foot of the back leg — and return to a standing position.
You can adjust the depth of movement by placing a short platform or stacked mats where your back knee contacts the ground. This will create a shorter range of motion so you can build strength and stability. Focus on sets of anywhere from six to 12 reps per leg, depending on your lower body health, strength, and conditioning.
Back Squat Form Tips
Of course, it’s worthwhile to go over the old classic. As far as squats go, the barbell back squat is the most ubiquitous “squat” you’ll ever see, but it’s also the most butchered. Let’s go over the checklist for an exercise that’s effective at training your quads, glutes, core, and total body mobility.
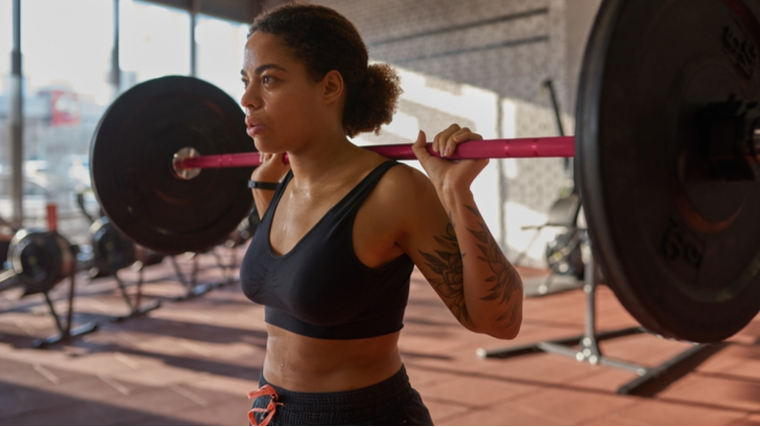

Let’s break things down step by step.
- Set the loaded bar in the rack at shoulder level and step underneath it. Position your hands just outside shoulder-width.
- Pull your shoulder blades back and bring your elbows slightly behind your body to create a perfect “shelf” to rest the bar on. Stand up under the bar so it’s comfortably positioned on that muscular shelf.
- Unrack the bark, take two steps backward, and even out your stance. You should be far enough away from the rack supports that you don’t crash into them on your descent or ascent.
- Try to pull the barbell apart. This will help you brace your entire upper body. Maintain this tension for the duration of your set. Get your feet ready in a comfortable, stable width and turn feet slightly out.
- Take a big breath in and brace your core — if your six-pack looks selfie-ready when you’re squatting, you’re doing it wrong. Get a big belly full of air and hold it for most of the repetition. Try to only let the breath out near the top of each rep.
- Descend slowly and under control. This will allow you to focus on tension, bracing, and alignment. Your knees should not cave inward. Instead, ensure they track in the same direction as your toes (slightly outward).
- Once you’ve descended with your thighs just below parallel, drive up strongly by squeezing your glutes. Aim for your shoulders to lead the way up, not your hips. The bar should travel in a straight line up and down, and your heels should remain planted.
Plenty of Squats, Plenty of Gains
Some lifters think a leg workout is incomplete without squats. That may or may not be true, but the bottomline is that some type of squat — whether it’s the classic back squat or any of the unique variations listed above — can be just the answer when you’re looking for a stronger lower body, more muscular legs, or improved mobility. Time to get some wheels.
References
- Burd, N. A., Andrews, R. J., West, D. W., Little, J. P., Cochran, A. J., Hector, A. J., Cashaback, J. G., Gibala, M. J., Potvin, J. R., Baker, S. K., & Phillips, S. M. (2012). Muscle time under tension during resistance exercise stimulates differential muscle protein sub-fractional synthetic responses in men. The Journal of physiology, 590(2), 351–362. https://doi.org/10.1113/jphysiol.2011.221200
Featured Image: Photology1971 / Shutterstock